Stagflation is a rare but serious economic condition that combines three major problems:
- High inflation
- Slow economic growth
- High unemployment
Understanding stagflation is important for investors, policymakers, and even regular citizens. In this blog, we’ll break down the term, explore its causes, provide examples, and explain how it impacts the Indian economy.
What is Stagflation?
It is a portmanteau of “stagnation” (no or slow growth) and “inflation” (increasing prices). In usual circumstances, inflation tends to be an indicator of a booming economy. However, when inflation increases when the growth falters and unemployment rises, it makes for an unhealthy economic landscape.
Key Characteristics of Stagflation
| Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Inflation | Persistent rise in prices of goods and services |
| Economic stagnation | Low or negative GDP growth |
| High unemployment | Many people lose jobs or can’t find new ones |
| Weak consumer demand | Consumers buy less due to job losses and price hikes |
What causes Stagflation?

It doesn’t occur often, but when it does, the effects are deep and long-lasting. Here are common causes:
Supply Shock
- A sudden increase in production costs—like oil prices—can reduce supply and raise prices.
Poor Economic Policies
- Overuse of money printing or faulty regulations can distort the economy and fuel both inflation and unemployment.
Global Slowdown
- Global economic crises (like the 2008 recession or a COVID-style disruption) can lead to slowdowns and price spikes.
Wage-Price Spiral
- Rising wages push prices up, which leads to further wage demands, creating an ongoing inflationary loop even when growth is slow.
Examples of Stagflation in History
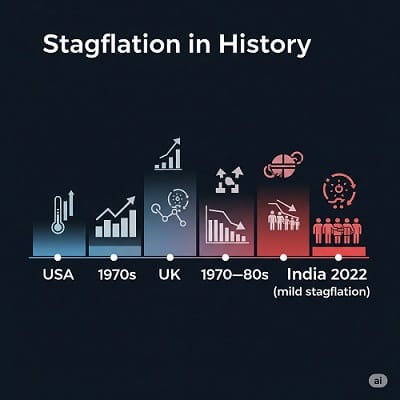
| Country | Period | Cause |
|---|---|---|
| USA | 1970s | Oil crisis, Fed policy errors |
| UK | 1970s–1980s | Energy shortages, labor unrest |
| India (mild form) | 2022 (post-COVID) | Supply chain crisis, food & fuel inflation |
How Stagflation Affects You
| Impact Area | Effect |
|---|---|
| Employment | Job losses or difficulty in finding new jobs |
| Household Expenses | Rising prices reduce purchasing power |
| Savings | Inflation reduces the real value of money kept in bank accounts |
| Investments | Stock markets may underperform, bonds may give poor returns |
| Borrowing | Interest rates may rise, making EMIs and loans expensive |
Is India at Risk of Stagflation?
As of 2024, India is not at the Risk of Stagflation, but has received the mild Symptoms
- Slower GDP growth in Q1 2023
- Rising Food and Fuel Price
- Moderate job Market Stress
However a strong Domestic demand,Govt capital spending,and Exports have prevented full blown Stagflation
What can be done to Prevent Stagflation?
| Action Area | Suggested Measures |
|---|---|
| Monetary Policy | RBI may raise interest rates to control inflation |
| Fiscal Policy | Govt can increase productive spending and reduce waste |
| Subsidies | Reduce burden of fuel, electricity costs on common citizens |
| Boost Employment | Invest in infrastructure and MSMEs to create jobs |
| Ease Supply Bottlenecks | Improve logistics, remove import/export restrictions |
How should investors react to Stagflation
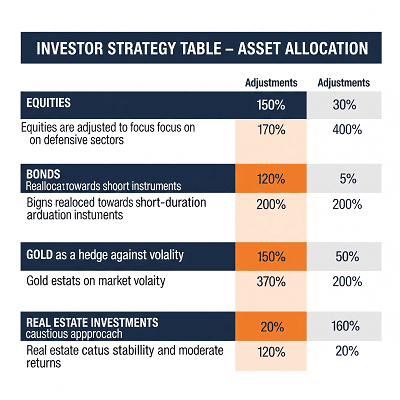
During stagflation,traditional portfolios suffers.Here’s how investor’s can re-balance
| Asset Class | Strategy |
|---|---|
| Equity | Focus on FMCG, pharma, utilities (non-cyclical) |
| Gold | Hedge against inflation |
| Bonds | Short-duration or inflation-indexed bonds |
| Real Estate | Cautious approach due to rising interest rates |
| Cash/Liquid Assets | Keep emergency funds in accessible instruments |
Conclusion
Stagflation is a tricky and tough economic situation that impacts all aspects of the economy—from the policy makers and investors to the ordinary man. Being informed, being frugal with finances, and prioritizing long-term planning is the key to staying shielded. India has proved itself to be resilient in the past and keeps making sensible moves to steer clear of such economic threats in the future