Rental Income: The Ultimate Guide for Landlords & Investors
Rental income is a common source of passive income for most investors, providing a stable cash inflow with the possibility of growth. If you are an experienced or new real estate investor, knowing the basics of rental income is one way of maximizing returns and abiding by tax regulations.
What Is Rental Income?

Rental income includes any payment received for the use or occupation of property. This would include regular rent payments and any additional amounts, such as advance rent, security deposits if retained, and lease cancellation payments. All rental income must be reported on your tax return, which is part of your taxable income.
Types of Rental Properties

- Residential Properties: These include single-family homes, apartments, and vacation rentals leased for dwelling purposes.
- Commercial Properties: Spaces rented for business activities, such as offices, retail stores, or industrial facilities.
- Mixed-Use Properties: Buildings that combine residential and commercial units.
Taxation of Rental Income in India

In India, rental income is primarily taxed under the category of ‘Income from House Property’ as per the Income Tax Act. The taxation process involves several key components:
- Gross Annual Value (GAV): This represents the highest of the property’s actual rent received, the municipal valuation, or the fair rent value.
- Deductions: The taxpayers are allowed deductions of municipal taxes paid in a year under GAV. Along with that, the taxpayers also get an exempt deduction of 30% (NAV) irrespective of their expenditure for repair and maintenance for that particular house. Home loans taken on interest payments on homes are also to be deducted from GAV.
- Taxable Income: After these deductions, the remaining amount is added to the total income of the individual and taxed according to the applicable income tax slab rates.
Residential rental income is exempt from Goods and Services Tax (GST), but GST may be levied on renting out commercial properties.
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) on Rental Income
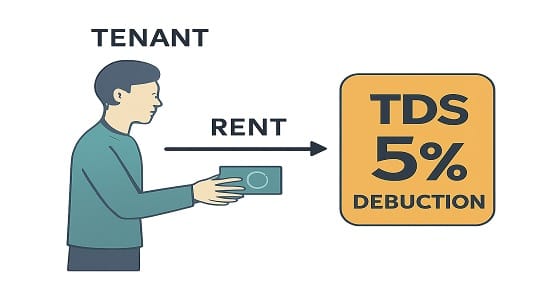
A tenant has to make a deduction of TDS at 5% under Section 194-IB if the rent paid every month crosses ₹50,000. This makes the tenant comply with tax and ensures that all the income earned is reported.
Strategies to Maximize Rental Income

To enhance rental income and achieve higher returns on investment, consider the following strategies:
- Property Selection: Invest in real estate located in more desirable areas, with good schools and low taxes and lots of other attractions. Be sure to locate areas with strong job markets and low crime rates to attract reliable tenants.
- Buy-and-Hold Strategy: Buy and hold real estate for long-term appreciation and rental income. Cash flow, property value growth, and tax deductions (e.g., depreciation, mortgage interest) are benefits
- Property Improvements: Renovating or up-gradation may justify higher rent to attract better quality tenants and thus improve property’s attraction.
- Effective Property Management: Proper property management can include maintenance of the property immediate redressal of tenant concerns, and adherence to legal requirements that ensure longer tenancy periods and lesser vacancy periods.
- Diversification: Invest in various types of properties or locations to spread the risk and leverage various market dynamics.
Tax Benefits and Deductions
Investors can leverage several tax benefits to optimize their rental income:
- Standard Deduction: A standard deduction of 30% on the Net Annual Value is allowed, irrespective of actual expenses incurred.
- Interest on Home Loan: Interest paid on a home loan for the rental property can be deducted from the rental income, reducing taxable income.
- Depreciation: Though not directly allowable under ‘Income from House Property,’ depreciation can be considered if the property falls under some other head of income, like ‘Income from Business or Profession.
Legal Considerations

Ensure compliance with local laws and regulations, including:
- Rental Agreements: Draft and put in place crystal clear comprehensive terms and conditions coupled with responsibility agreement between parties with regard to all the matters for an agreement.
- Tenant Verification: to verify their worthiness before finally renting a building to any
- Registration: as this is again complied with, duly registered before authorities to have lawfully agreed rentals.
Challenges in Rental Income

While rental income provides many advantages, investors may face problems like:
- Vacancy Periods: Vacant properties mean lost income.
- Maintenance Costs: Repairs and maintenance can be expensive and reduce the profit margin.
- Tenant Management: Handling problematic tenants or disputes requires time and energy.

“Landlords grow rich in their sleep.”
