The IPO Handbook: Your Roadmap to Successful Investing
If you follow the stock market, you must have seen the buzz around big IPOs like Zomato, Nykaa, and LIC. But what exactly is an Initial Public Offering, and how can you invest in it? An Initial Public Offering is when a company offers its shares to the public for the first time.
This not only helps the company raise capital but also gives retail investors like you the opportunity to own a part of the company. In India, the IPO process is regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), ensuring transparency and fairness. In this blog, we’ll break down types of Initial Public Offerings, why companies go public, how to invest, allotment process, and key factors to consider before investing — in simple language that every investor can understand..
Types Of IPO (Initial Public Offering)
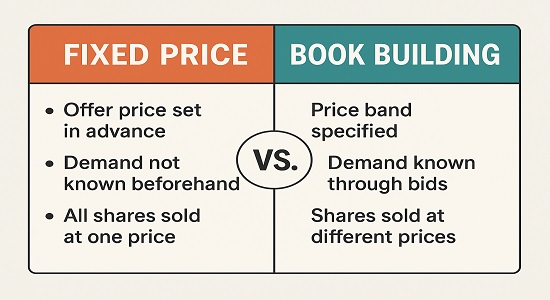
Fixed Price Offering
- In this type, the company decides a fixed price before the it opens.
- Investors know exactly how much they need to pay per share.
- Example: If the fixed price is ₹500 and the lot size is 30 shares, you invest ₹15,000
Book Building
- Here, the company provides a price band (say ₹500–₹550).
- Investors bid within this range.
- The final price, called the cut-off price, is decided based on demand.
- This is the most common method in India (e.g., Zomato IPO).
Why Do Companies Go Public
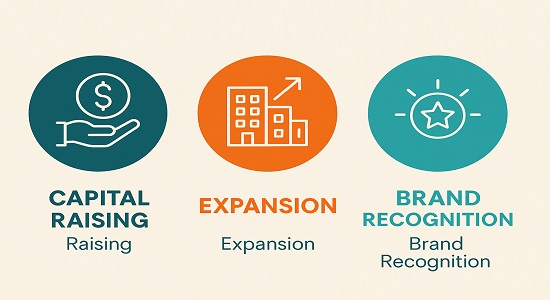
Companies launch IPOs mainly to raise money for:
- Expansion: Entering new markets, building factories, or acquiring competitors.
- Debt Repayment: Reducing loans and improving balance sheet strength.
- Brand Recognition: A listed company enjoys higher trust.
- Liquidity for Promoters/Investors: Early investors (VCs, angels) can sell shares in IPOs.
How to Invest in an IPO

- Open a Demat Account:
- Mandatory to apply for IPO shares.
- Open with any SEBI-registered broker (e.g., Zerodha, Upstox, Groww).
2. Select the IPO:
- Check the company’s prospectus (DRHP) available on SEBI/NSE/BSE websites.
- Understand its business model, risk factors, and objectives.
3. Make a Bid:
- IPOs have a lot size (minimum shares).
- Place your bid within the price band.
- Option to choose cut-off price (best for retail investors).
4. Payment via ASBA:
- Funds are blocked in your bank account via Application Supported by Blocked Amount (ASBA).
- No money is deducted unless you are allotted shares.
5. Allotment of Shares:
- If it is oversubscribed, allotment is done via a lottery system.
- Retail quota is usually 35% of total shares.
- If you don’t get allotment, money is automatically released back to your account.
Factors to Consider Before Investing in an IPO

- Lot Size: Minimum number of shares you can bid for.
- Price Band: Range within which you must bid.
- Over-subscription Risk: More demand = lesser chances of allotment.
- Bid Flexibility: You can revise bids during the its window.
Factors to Consider Before Investing in an IPO
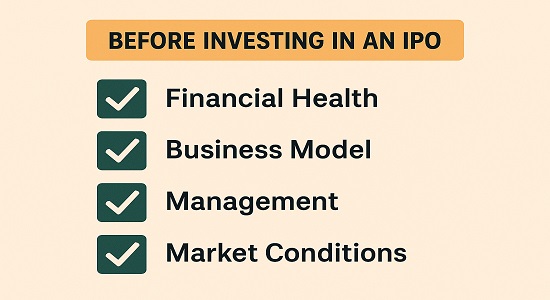
Company’s Financial Health :
- Revenue growth, profit margins, debt ratio.
- Example: Zomato had high revenue growth but was loss-making, yet still got huge demand.
- Business Model – Is it scalable and future-ready? Tech-enabled and consumer-driven models attract higher valuations.
- Management Team – Leadership quality and past track record.
- Prospectus Analysis – Read the DRHP carefully for risks and opportunities.
- Growth Prospects – Industry demand and market expansion opportunities.
- Market Conditions – When launched in a bull market generally perform better.
Risks in IPO Investment

- Volatility: Prices may fall post-listing. Example: Paytm listed below issue price.
- Hype Factor: Not every “famous brand” IPO is profitable.
- Lock-in for Promoters: Sometimes promoters sell quickly, creating selling pressure.

Conclusion
It can be a great way for retail investors to participate in a company’s growth story from the beginning. However, it’s important to research, evaluate financials, and not get carried away by hype.
If you are a beginner, start small and learn the process by applying for popular IPOs. Over time, you’ll develop the judgment to pick the right ones.
I like this web site very much so much good information.